Search Results
Results for: 'organic molecule'
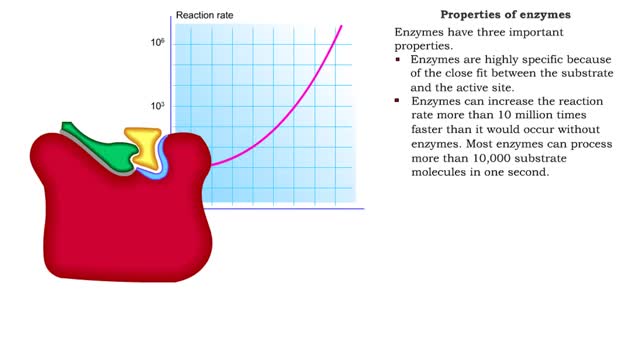
Enzyme structure - Properties of enzymes
By: HWC, Views: 10978
■ Enzymes are proteins that catalyze reactions. ■ Some enzymes have two parts: a protein or apoenzyme and a non-protein or cofactor. ■ Cofactor can be a metal ion or another organic molecule called a coenzyme. ■ Coenzymes often come from vitamins. ■ Cofactors affect the shape of...
By: HWC, Views: 5611
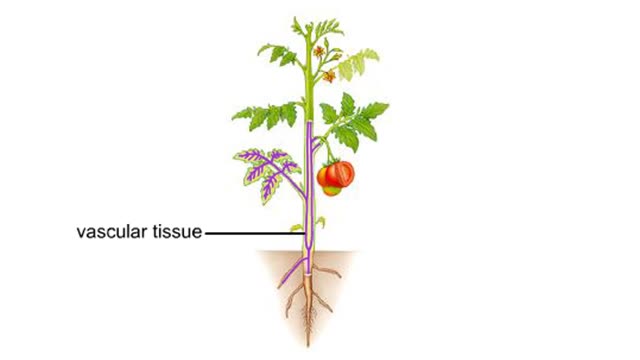
The bulk of the plant body is comprised of ground tissue. Vascular tissue threads through the ground tissue. It distributes water, solutes, and organic substances through the plant body. Dermal tissue covers and protects the surfaces of the root and shoot systems.
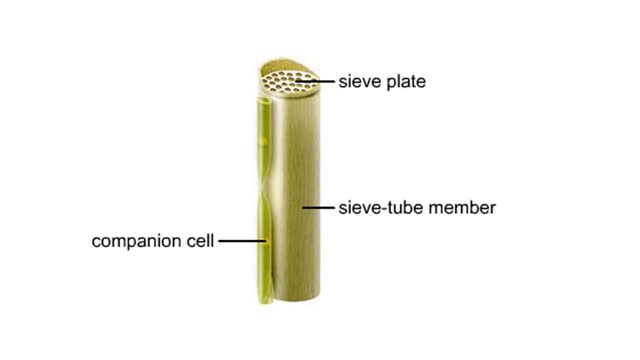
Vascular tissues in a corn stem and a buttercup root
By: HWC, Views: 5508
Vascular tissues in a corn stem and a buttercup root. The cells that make up each tissue. Xylem conducts water and dissolved ions. It also helps mechanically support a plant. The cells, called vessel members and tracheids, are dead at maturity. Their lignified walls interconnect and serve as p...
By: HWC, Views: 10528
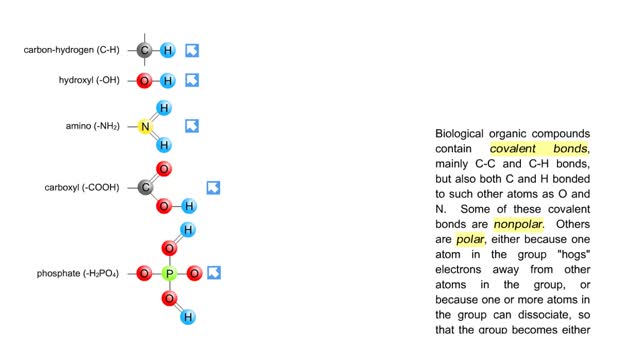
Biological organic compounds contain covalent bonds, mainly C-C and C-H bonds, but also both C and H bonded to such other atoms as O and N. Some of these covalent bonds are nonpolar. Others are polar, either because one atom in the group "hogs" electrons away from other atoms in the group, or...
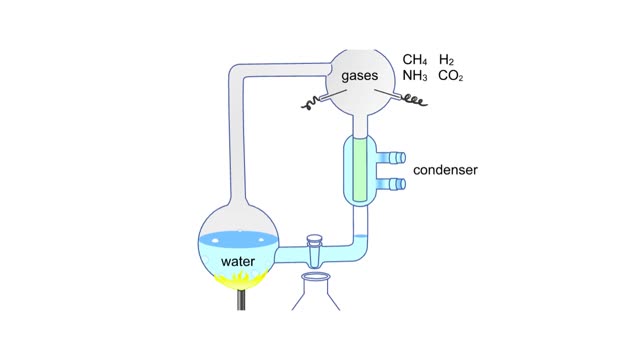
Miller's reaction chamber experiment Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4732
A simple diagram of Stanley Miller and Harold Urey's experimental apparatus. The lower portion of the apparatus was filled with water. The upper portion was filled with a mixture of gases that simulated the earth's early atmosphere. Examples are methane, ammonia, hydrogen and carbon dioxide. ...
By: HWC, Views: 5035
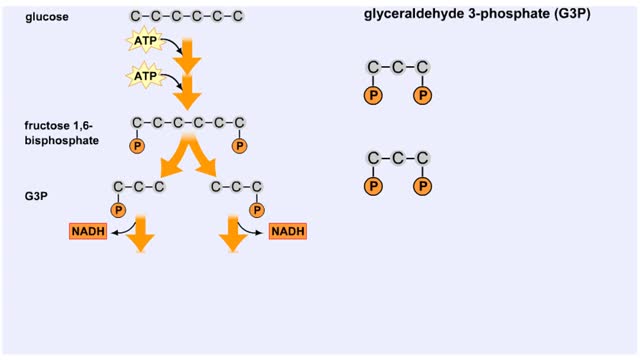
In glycolysis, a six-carbon glucose molecule is split into two three-carbon pyruvate molecules. In this animation, each carbon molecule is represented by a red ball. The end products of glycolysis are two molecules of pyruvate. Glycolysis is the breakdown of glucose into two molecules of ...
What Are Carbohydrates? Importance of Carbs & High Carb Food
By: HWC, Views: 11183
We hear a lot about carbohydrates in the news. Everybody seems to be on a low-carb diet. The news media often has stories on this diet fad, and companies are busy producing products with reduced carbohydrates. What's this fascination with carbohydrates? In a word: "Diet." The fact is that carb...
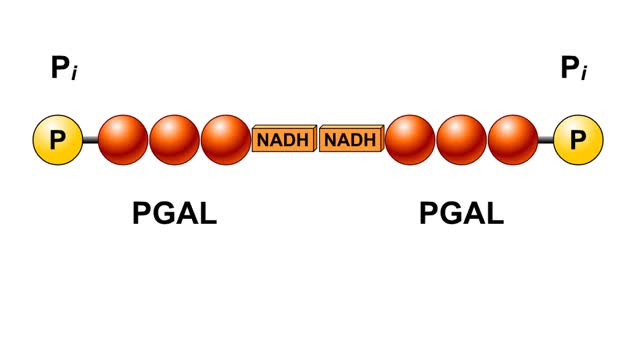
Splitting of Sugar, Oxidation/ Reduction & ATP Generation
By: HWC, Views: 10770
The next reaction shows us the meaning of "glycolysis" or the splitting of glucose. The fructose bisphosphate molecule is split into two molecules each containing 3 carbons as the backbone. FBP is split into two 3-carbon molecules called G3P, or glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. Notice that the phos...
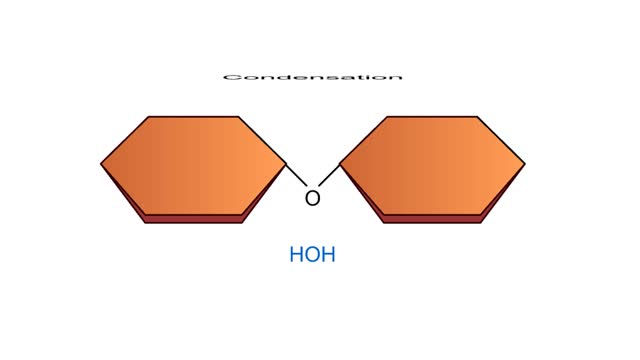
Condensation and Hydrolysis Animation
By: HWC, Views: 4827
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together to form one larger molecule. An enzyme removes a hydroxyl group from one molecule and a hydrogen atom from another, then speeds the formation of a bond between the two molecules at their exposed sites. Typically the discarded atoms join t...
Advertisement